Tag: cell biology

What is the function of the cell membrane?
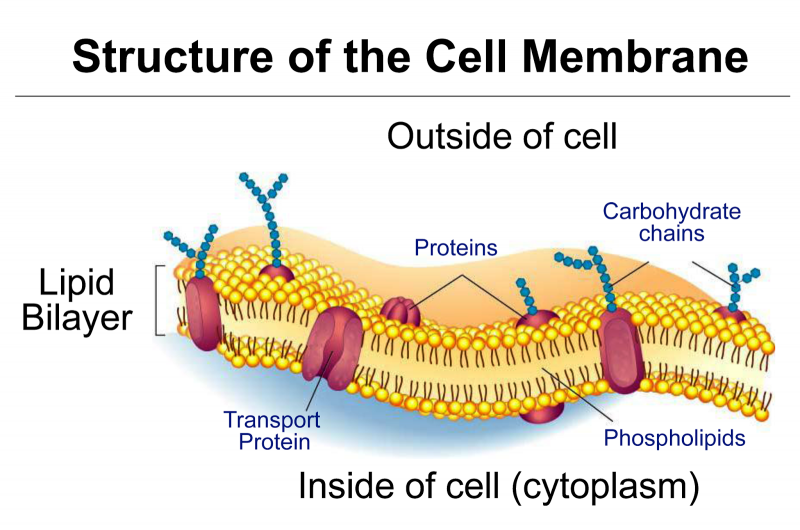
The cell membrane is otherwise called a Plasma membrane. It may be defined as the thin, elastic, semipermeable living membrane that serves as a boundary for the Cytoplasm. The Cell membrane is made up of glycoproteins and phospholipids. The Functions of the Cell membrane are as follows: Cell membrane or Plasma membrane is a semipermeable membrane present…

Q & A ON REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
Q1. What is life span? Ans: Life span is the period from birth to natural death of an organism. Q2. Define clone. Ans: The individuals that are morphologically and genetically similar to the parent are called clone. Q3. Mention the different means/ methods of asexual reproduction with example. Ans: Cell division – Protista, Monera Binary…

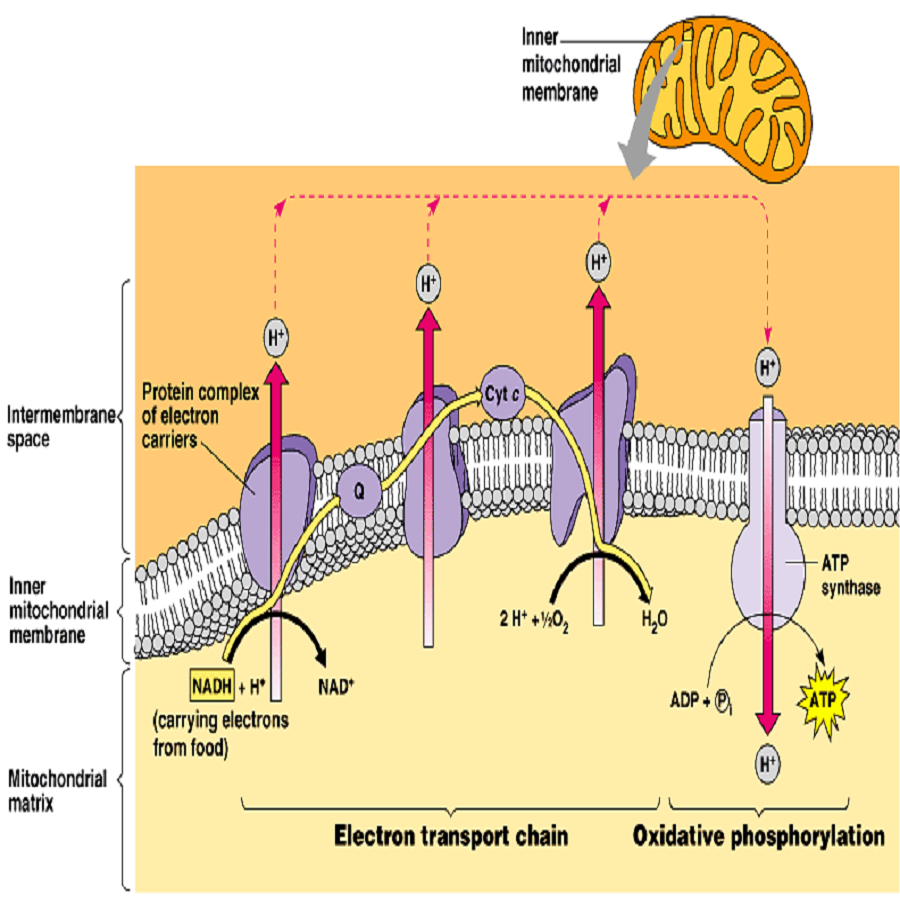
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION, ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION It is the main source of energy of our cell. Takes place in Mitochondria. Movement of protons through inner mitochondrial membrane leads to ATP production DEFINITION Oxidative phosphorylation includes the coupling of the oxidation of NADH or FADH2 by the respiratory chain with the synthesis of ATP via gradient of protons across the inner mitochondrial…

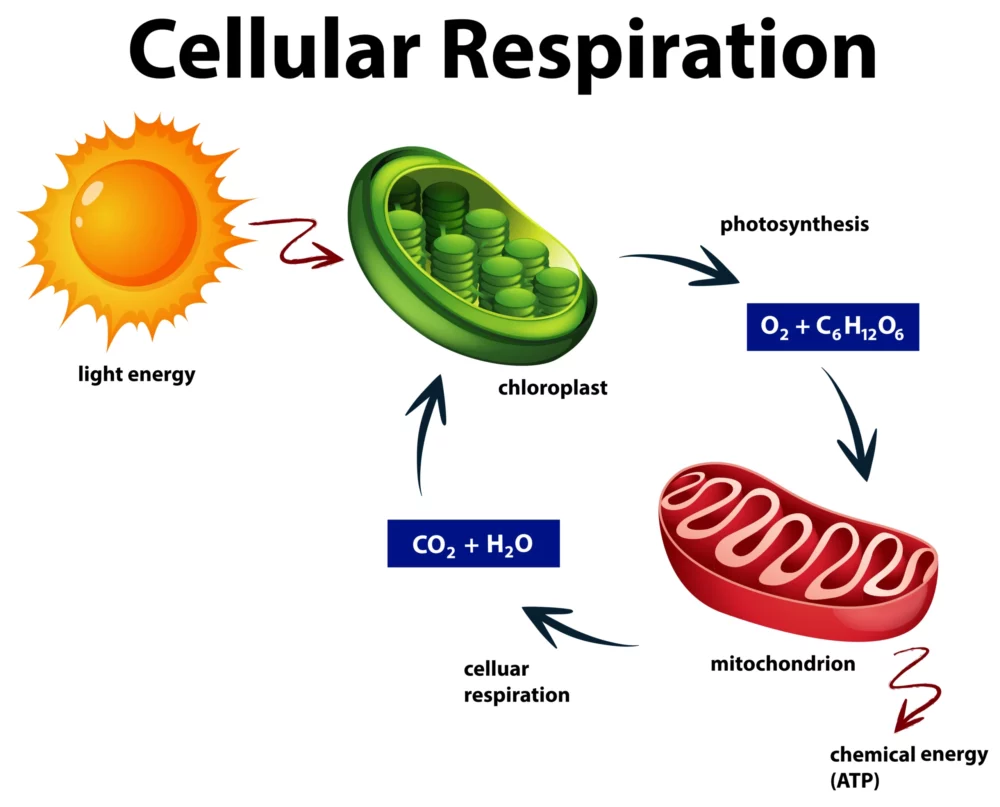
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Cellular respiration is a fundamental biochemical process that occurs in all living cells, from the tiniest bacteria to the most complex multicellular organisms. It is the means by which cells convert organic molecules, primarily glucose, into adenosine triphosphate (ATP) – the universal currency of cellular energy. This intricate and highly regulated metabolic pathway is essential…

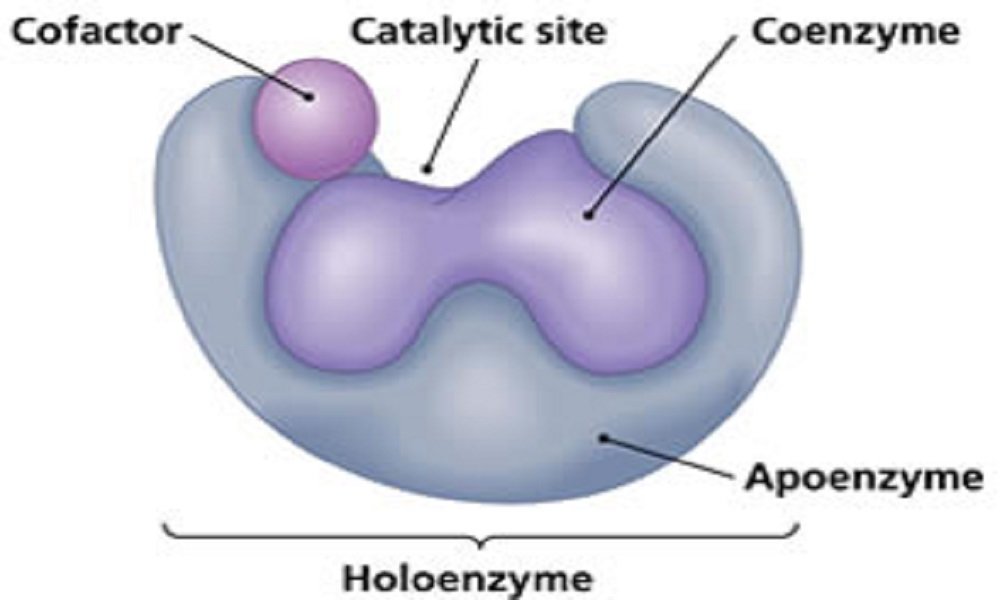
COENZYMES
Enzymes may be simple proteins or complex enzymes. A complex enzyme contains a non-protein part, called a prosthetic group (co-enzymes). Coenzymes are heat stable low molecular weight organic compound. The combined form of protein and the co-enzyme are called as holo-enzyme. The heat labile or unstable part of the holo-enzyme is called as apo-enzyme. The…

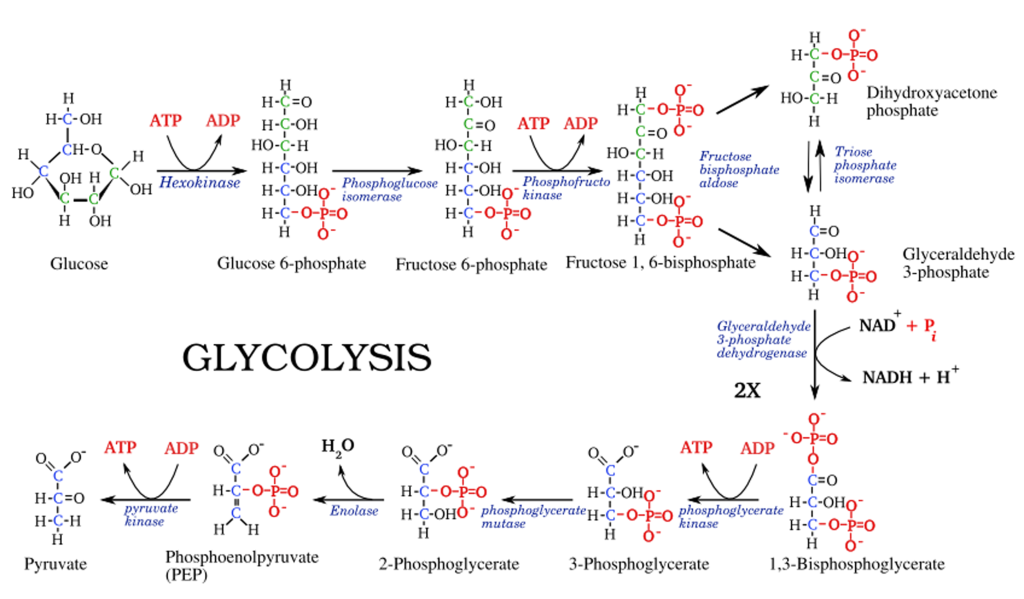
Glycolysis Pathway
Glycolysis is a crucial metabolic pathway found in all living cells, serving as the initial step in the breakdown of glucose to produce energy. This ancient and highly conserved process occurs in the cytoplasm and plays a central role in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. In this note, we’ll delve into the details of glycolysis,…

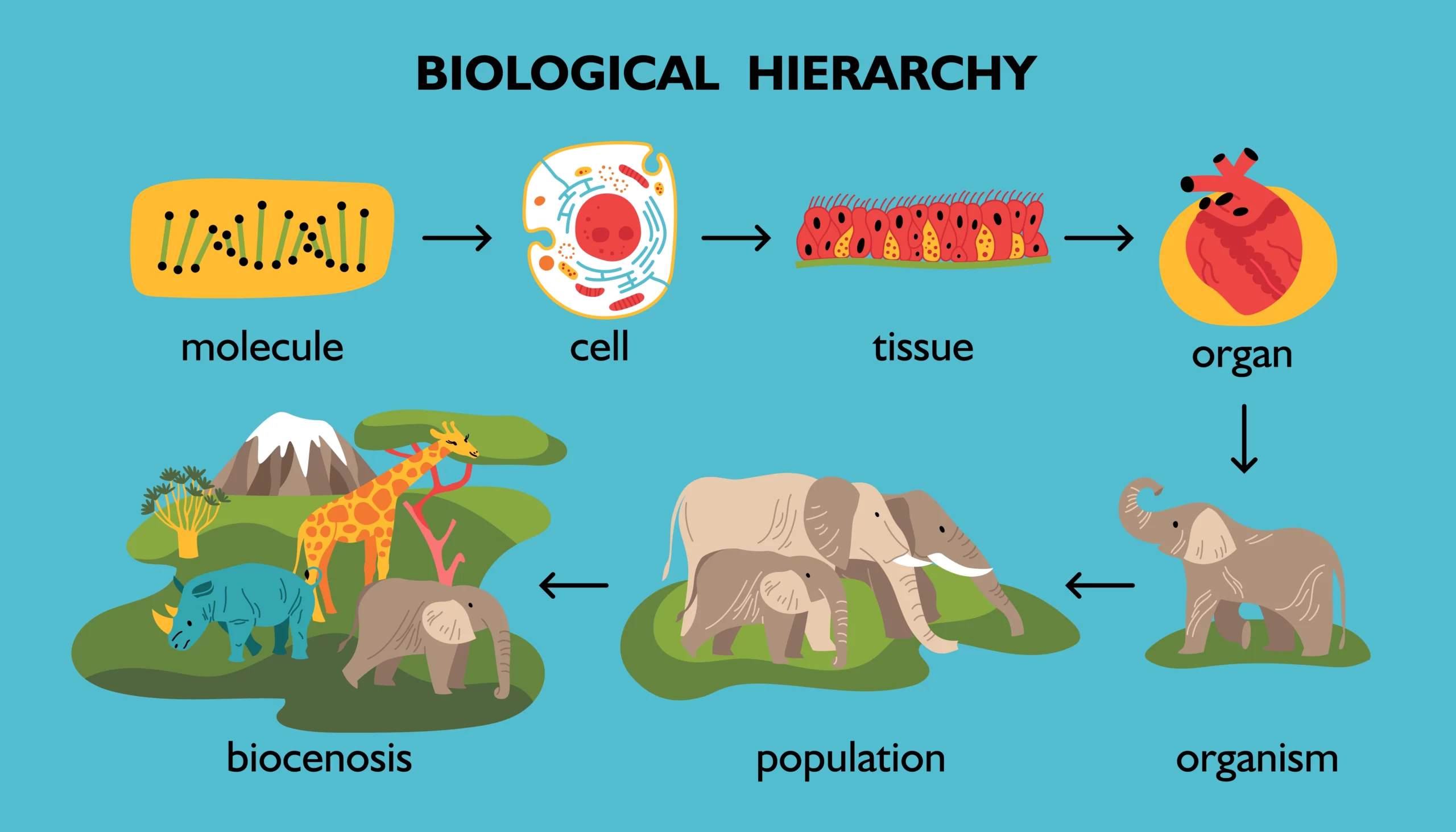
Biological Classification
Biological Classification: Understanding the Diversity of Life In the vast tapestry of life that envelops our planet, organisms of all shapes, sizes, and functions coexist. From the towering trees of the rainforests to the microscopic bacteria hidden in the soil, every living entity has a place and role in the intricate web of life. This…

Genetics
Genetics: Unveiling Life’s Blueprint In the realm of genetics, we dive into the complex domains of genes, heredity, and trait inheritance. This captivating field untangles the intricacies of life’s diversity and continuity. It unveils aspects ranging from eye color to susceptibility to diseases. Genes and Heredity: Genes, those DNA segments, house the instructions steering growth,…

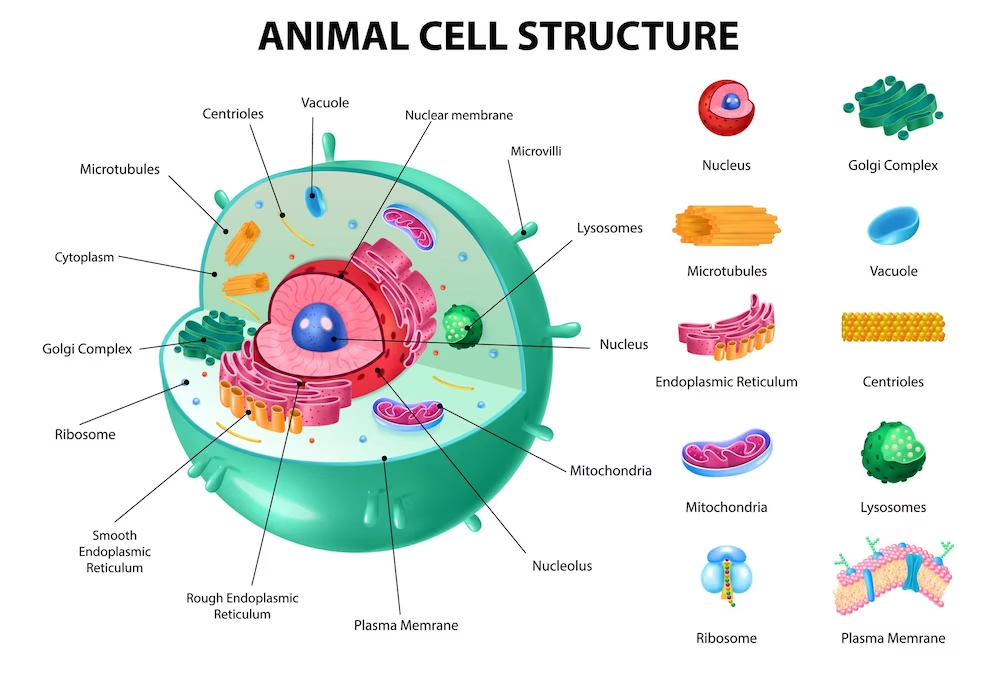
WHAT IS CELL?
A cell is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life and serves as the building block of all living things. Cells are incredibly diverse in terms of their structure and function, yet they all share common characteristics that define them as cells. Here are…