Tag: cell biology

General Q&A part-2
This page contains general Q&A questions asked by curious people. What is biochemistry? Biochemistry is a branch of science that combines principles from both biology and chemistry to study the chemical processes and substances that occur within living organisms. It focuses on understanding the molecular mechanisms that underlie various biological functions and processes, including metabolism,…

Enzymes: Substrate Interaction & Biochemistry
Within the realm of biology, cells rely on intricate processes to sustain life. Catalysts known as proteins play a crucial role in these processes, expediting chemical reactions. These proteins possess a remarkable capability to interact with specific substances, forming the foundation of biochemistry. In this article, we will explore these proteins and their interactions with…

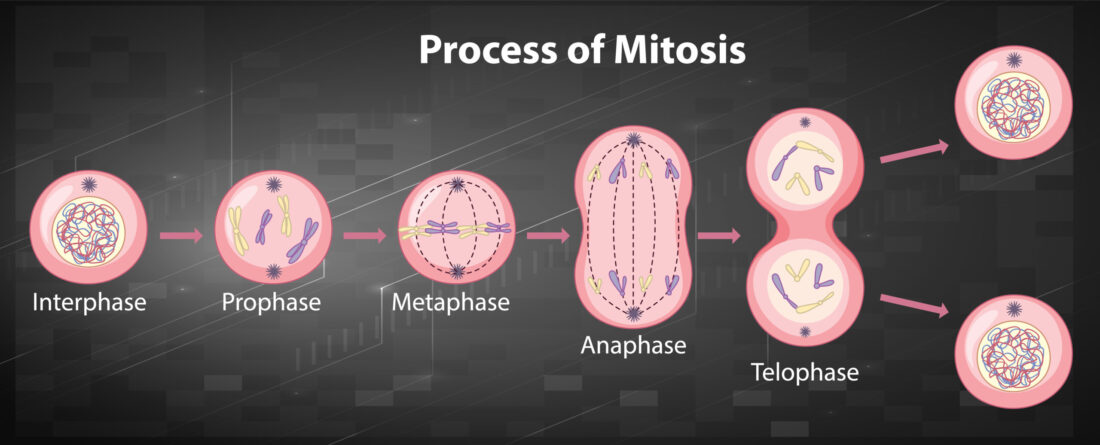
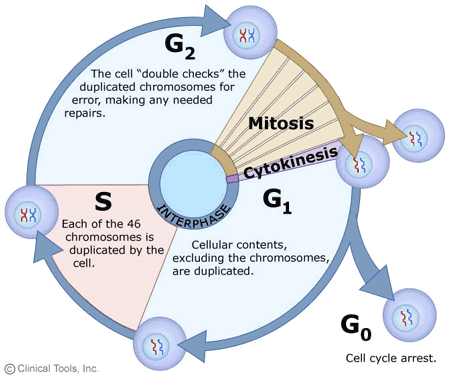
Mitosis: A Comprehensive Explanation of Each Stage and Its Vital Role in Cell Division
Mitosis is a fundamental process of cell division in which a single eukaryotic cell divides into two identical daughter cells, each containing the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This process is crucial for growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction in multicellular organisms. Mitosis consists of several distinct stages, each with its own…

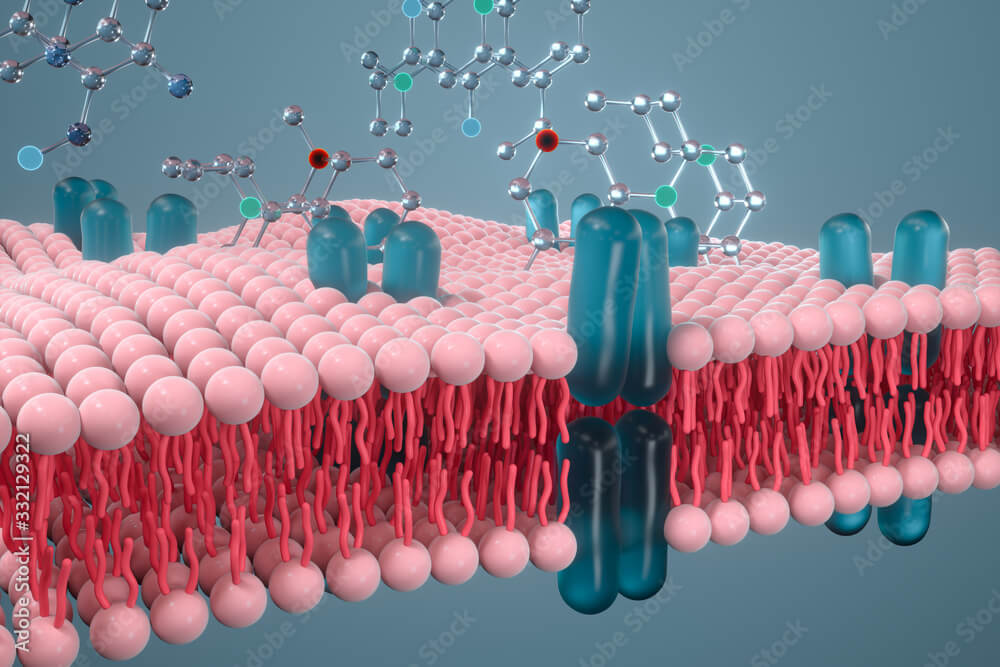
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function: Key Role in Cell Homeostasis
The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, is a crucial structure that surrounds all living cells. It separates the internal environment of the cell from the extracellular environment, regulating the flow of substances in and out of the cell. The plasma membrane plays a central role in maintaining cell homeostasis, which is the…

Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of the Immune System
1) What is the primary function of the immune system? a) Digestion of food b) Regulation of body temperature c) Protection against infections and diseases d) Production of hormones Answer: c) Protection against infections and diseases Explanation: The immune system’s main role is to defend the body against harmful pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi,…

What is the role of hemoglobin?
The Crucial Role of Hemoglobin in Your Body Hemoglobin is an unsung hero in your body’s complex orchestra of functions. This iron-rich protein plays a central role in sustaining life by carrying oxygen to every cell. Let’s delve into the fascinating functions of hemoglobin and why it’s essential for your well-being. Oxygen Transport – Hemoglobin’s…

What is enzyme and characteristics?
Enzymes are biological catalysts that facilitate chemical reactions in living organisms. They are typically proteins, although some RNA molecules also have catalytic activity. Enzymes are essential for life because they speed up the reactions that are necessary for cells to function properly. Without enzymes, many biochemical reactions in the body would occur too slowly to…

MCQ on Breathing and Exchange of Gases-2
Visiting high mountains may cause altitude sickness in men living in plain areas. Prime cause of this is (a) excess of CO2 in blood (b) decreased efficiency of haemoglobin (c) decreased partial pressure of oxygen (d) decreased proportion of oxygen in air. Increase in body temperature makes oxygen haemoglobin dissociation curve (a) shift to left…

Chromosome
A chromosome is a structure found in cells that is made up of a long strand of DNA, which is the genetic material that contains the instructions for the development and function of all living organisms. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and play a crucial role in the cell cycle, replication,…

MCQ on Respiration in plant
Q1: Which organelle in plant cells is primarily responsible for cellular respiration? (A) Chloroplast (B) Mitochondrion (C) Vacuole (D) Nucleus Answer: (B) Mitochondrion Explanation: Mitochondria are the main sites of cellular respiration in plant cells, where ATP is produced. Q2: During respiration, what is the primary substrate used by plants to generate energy? (A) Oxygen…
Active Transport
A few ions or molecules are transported across the membrane against their concentration gradient, i.e., from lower to higher concentration. Such type of transport is called active transport because it is an energy-dependent process in which ATP is utilised, e.g., Na+/K+ pump. https://youtu.be/visqfZd7Ms4 Active transport uses energy to pump molecules against a concentration gradient. Active…

Q & A ON CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION
Q 1. Define cell cycle Ans. The sequence of events by which cell duplicates its genome, synthesis of other constituents of the cell and eventually divides into two daughters cell. Q2. Name the phases of cell cycle Ans. A) Interphase B) M Phase Q3. What is the G1phase of the interphase? Ans. The G1 phase Corresponds to interval…