Delimiting membrane or boundary of all cells providing the characteristic shape to the cell.
Structure
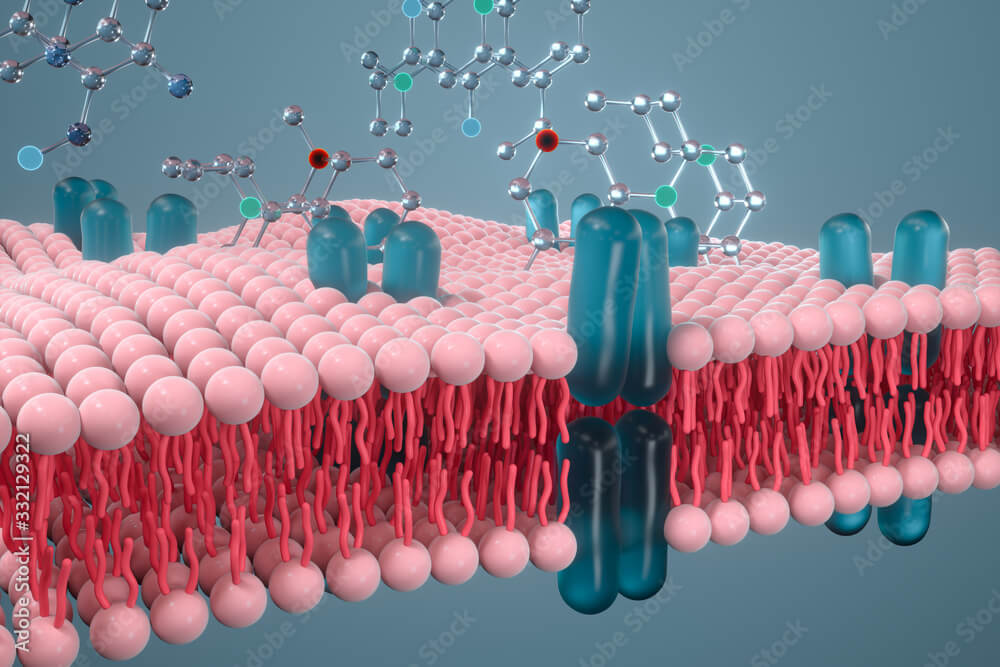
● Composed of approx. 7 nm thick phospholipid bilayer with hydrophilic heads facing outward from both sides into aqueous environment and hydrophobic tails facing inside the bilayer.
● A symmetrical the presence of proteins, floating in the bilayer imparts a fluid mosaic pattern which comprises of
(a) Integral/Intrinsic proteins spanning through the lipid bilayer, protruding both extracellular and cytoplasmic sides of membrane.
(b) Peripheral/Extrinsic proteins located on outside either extracellular or cytoplasmic surface.
(c) Lipid anchored proteins covalently linked to a lipid molecule of bilayer but present
outside to it.
● Some oligosaccharides are covalently linked to both protein and lipid components forming glycoproteins and glycolipids, respectively facing outward into the extracellular environment.
● Cholesterol molecules aligned with the fatty acyl chains of phospholipids, increases the permeability and fluidity of membrane. The presence of cholesterol molecules at moderate temperatures also prevents membrane solidification at cold temperatures.
● Membrane shows fluidity by exhibiting flexing, flip flop, rotation and lateral diffusion movements.
Functions
● Compartmentalisation
● Transportation of selective molecules in and out
of the membrane, i.e. active and passive transport (diffusion and osmosis), recognition of substances and hormones and cell adhesion and recognition
Some specialised functions of plasma membrane in different regions of cell are
Apical Plasma Membrane
● Regulation of nutrient and water intake
● Regulated secretion
● Protection
Lateral Plasma Membrane
● Cell contact and adhesion
● Cell communication
Basal Membrane
● Cell-substratum contact
● Generation of ion gradients




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.