One stop solution for all your biology questions!

ORIGIN OF LIFE
The earth was formed about five billion years ago. At that time it was extremely hot. The existence of life in any form at that high temperature was not possible. As such, two questions arise pertaining to life: 1. How did life originate on earth? 2. How did primitive organisms evolve into new forms resulting…

ENZYMES
The global life depends on a series of chemical reactions. Most of the chemical reactions proceed too slowly on their own to sustain life. Hence catalysts are required to greatly accelerate the rates of these chemical reactions. In nature enzymes posses the catalytic power to facilitate life processes in essentially all life-forms from viruses to…

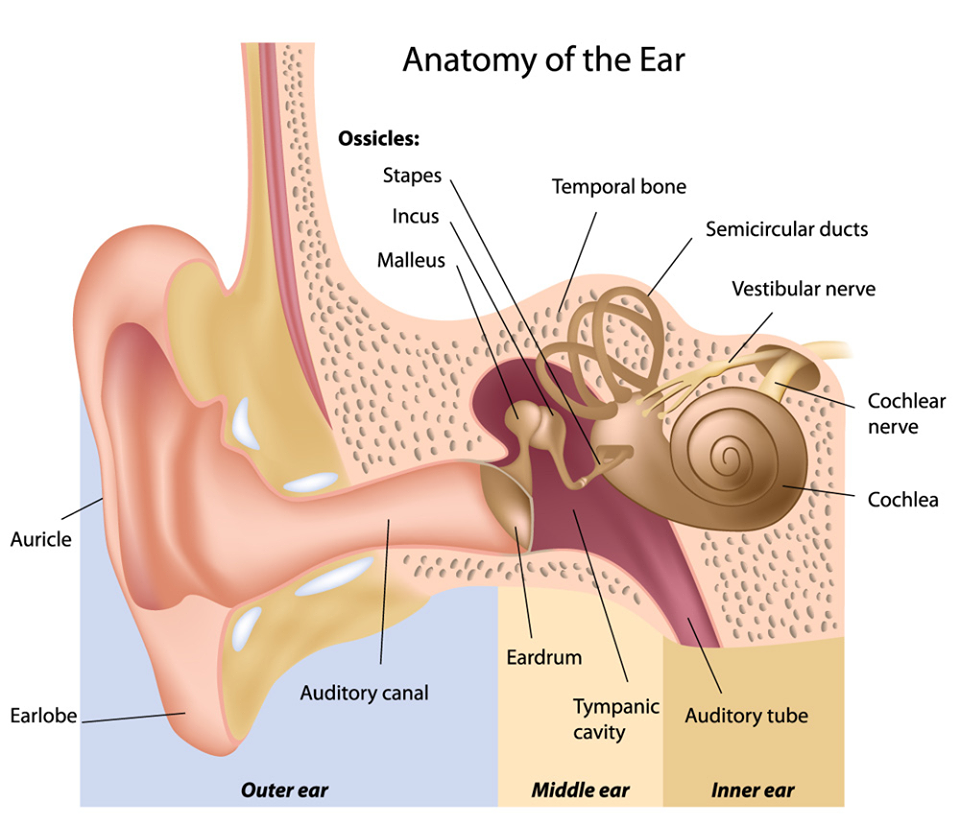
EAR ANATOMY
The ear is the organ found in animals which are designed to perceive sounds. Most animals have some sort of ear to perceive sounds, which are actually high-frequency vibrations caused by the movement of objects in the environment. The human ear picks up and interprets high-frequency vibrations of air, while the sound-sensing organs of aquatic…

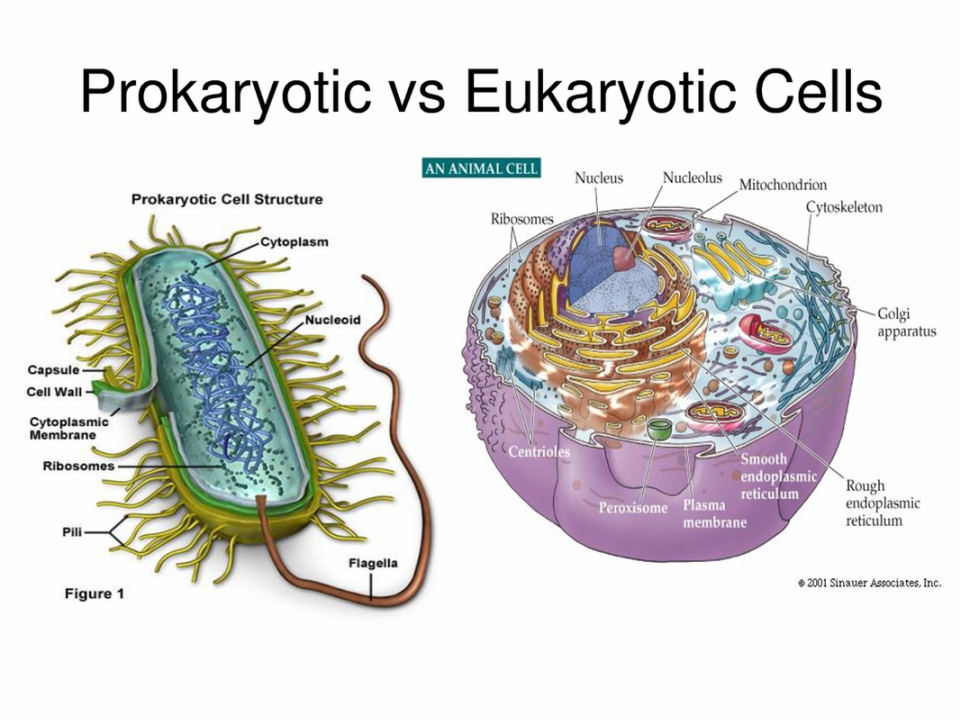
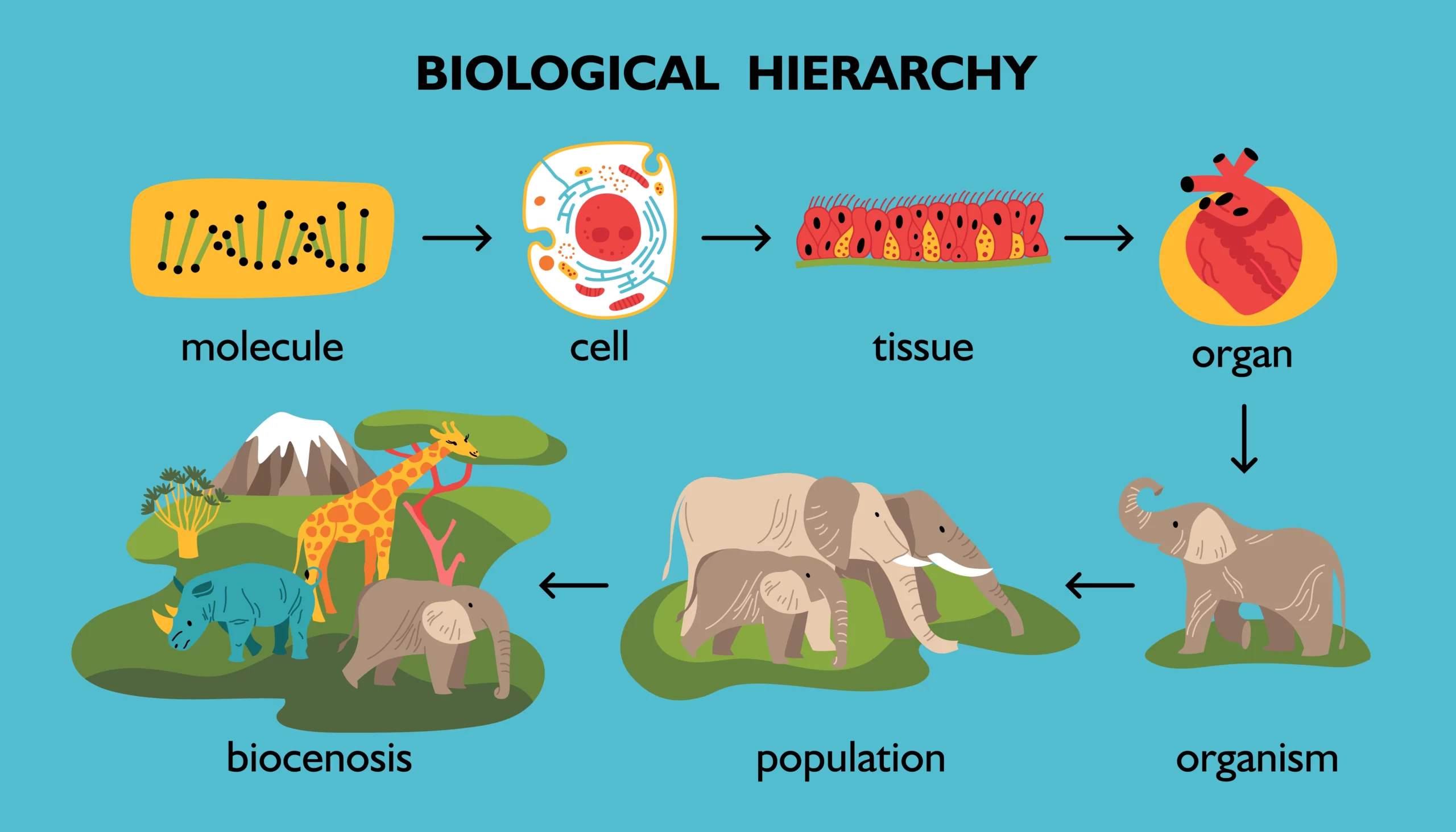
THE CELL AND CELL THEORY
Landmarks in the study of a cell Soon after Anton Van Leeuwenhoek invented the microscope, Robert Hooke in 1665 observed a piece of cork under the microscope and found it to be made of small compartments which he called “cells” (Latin cell = small room). In 1672, Leeuwenhoek observed bacteria, sperms and red blood corpuscles,…
COMPONENTS OF THE CELL
The major components of the cell are cell membrane cytoplasm nucleus Cell membrane (Plasma membrane) Each cell has a limiting boundary, the cell membrane, plasma membrane or plasmalemma. It is a living membrane, outermost in animal cells but internal to cell wall in plant cells. It is flexible and can fold in (as in food vacuoles…

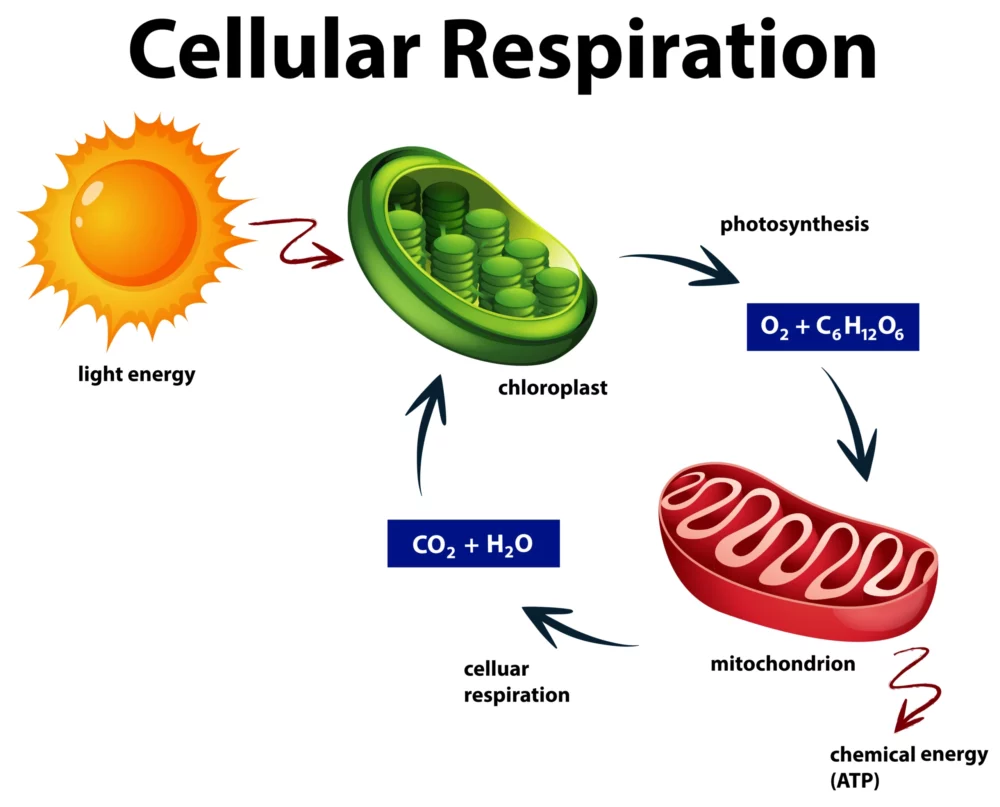
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Cellular respiration is a fundamental biochemical process that occurs in all living cells, from the tiniest bacteria to the most complex multicellular organisms. It is the means by which cells convert organic molecules, primarily glucose, into adenosine triphosphate (ATP) – the universal currency of cellular energy. This intricate and highly regulated metabolic pathway is essential…

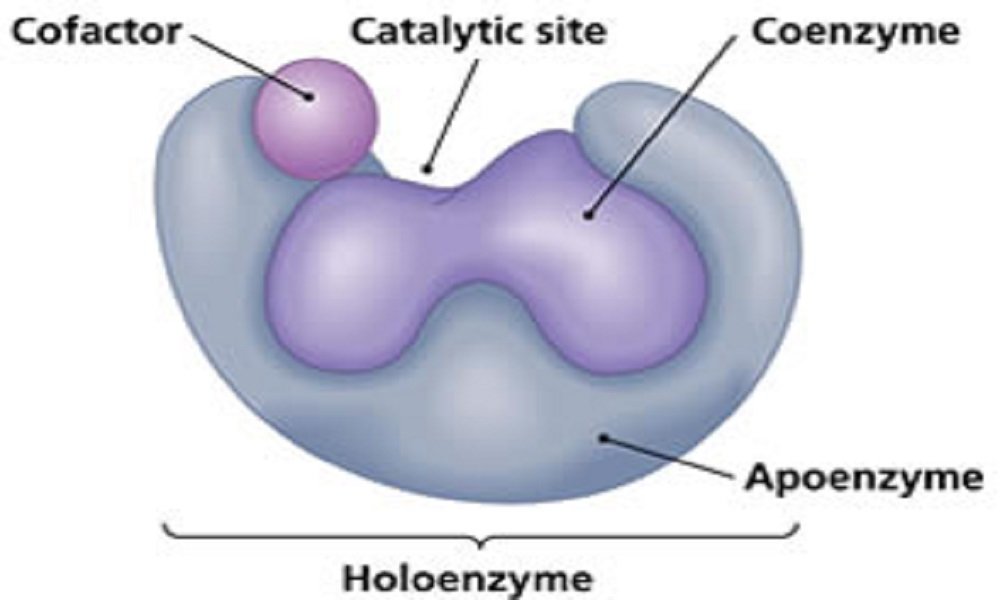
COENZYMES
Enzymes may be simple proteins or complex enzymes. A complex enzyme contains a non-protein part, called a prosthetic group (co-enzymes). Coenzymes are heat stable low molecular weight organic compound. The combined form of protein and the co-enzyme are called as holo-enzyme. The heat labile or unstable part of the holo-enzyme is called as apo-enzyme. The…

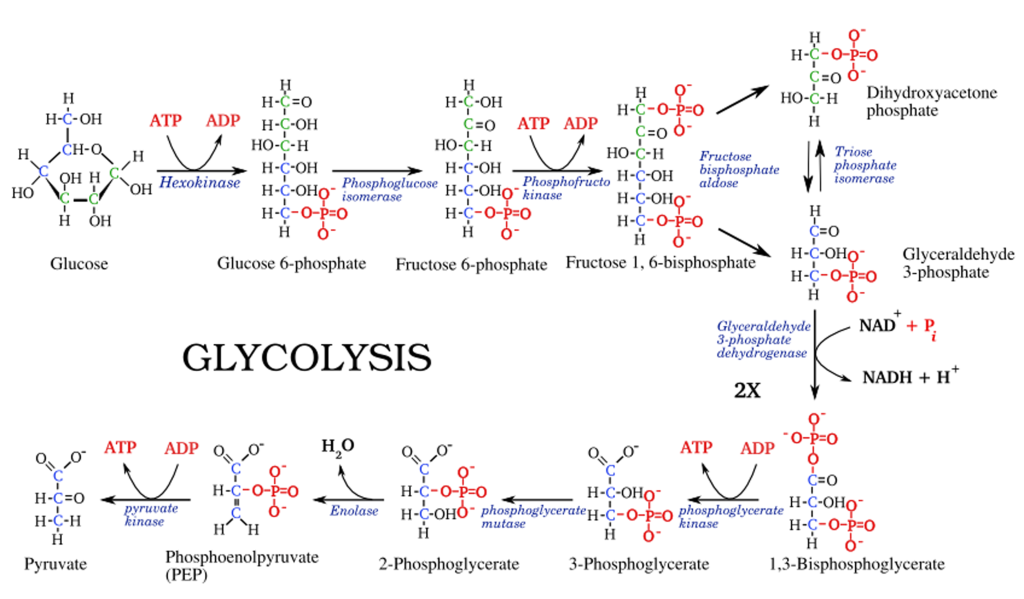
Glycolysis Pathway
Glycolysis is a crucial metabolic pathway found in all living cells, serving as the initial step in the breakdown of glucose to produce energy. This ancient and highly conserved process occurs in the cytoplasm and plays a central role in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. In this note, we’ll delve into the details of glycolysis,…

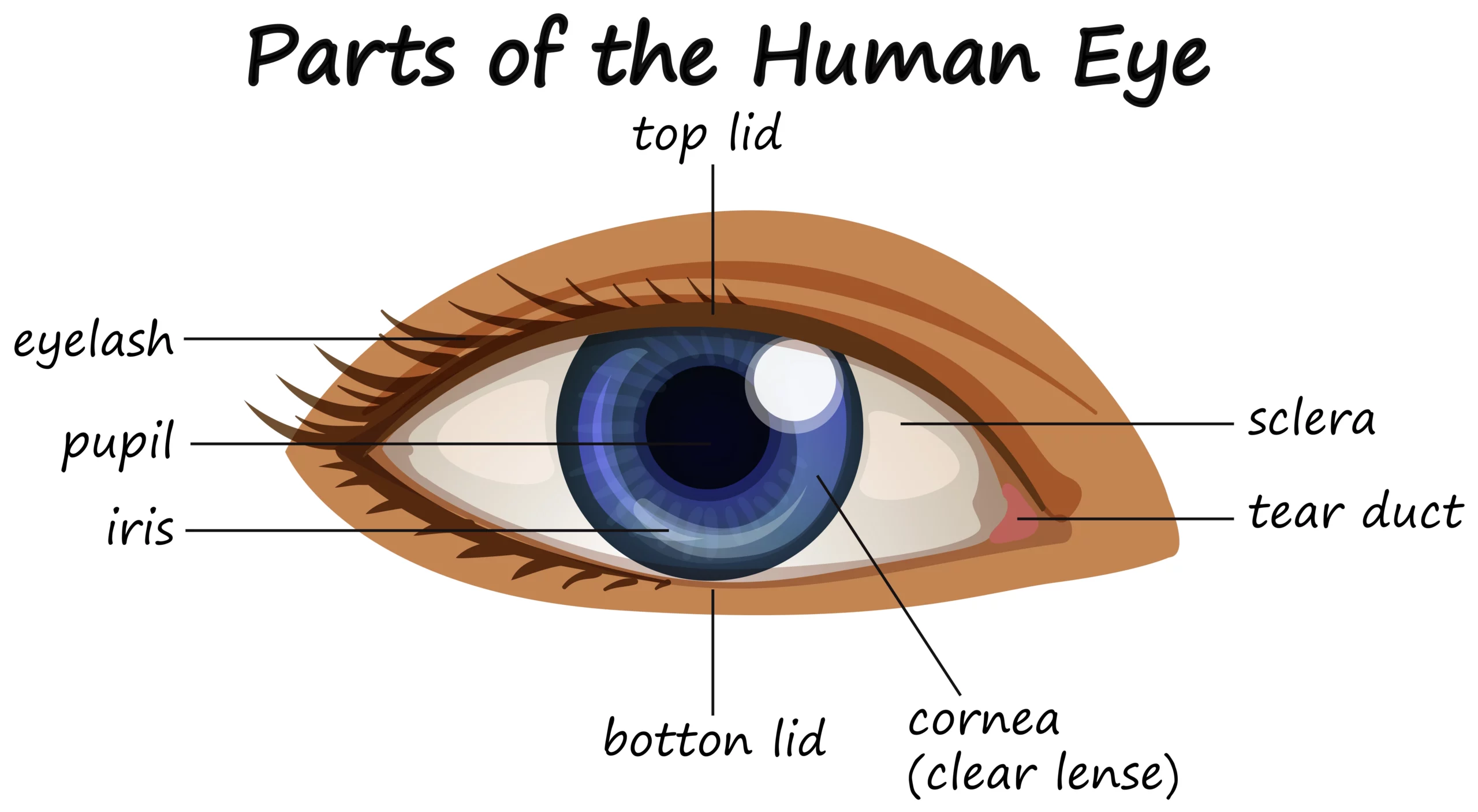
Human Eye: Anatomy, parts and structure
Exploring the Human Eye: Unveiling its Anatomy, Parts, and Structure The human eye is a marvel of complexity and precision, allowing us to perceive the vibrant world around us. From the simplest forms of light detection to the intricate details of color and depth perception, the eye plays a pivotal role in our sensory experience.…

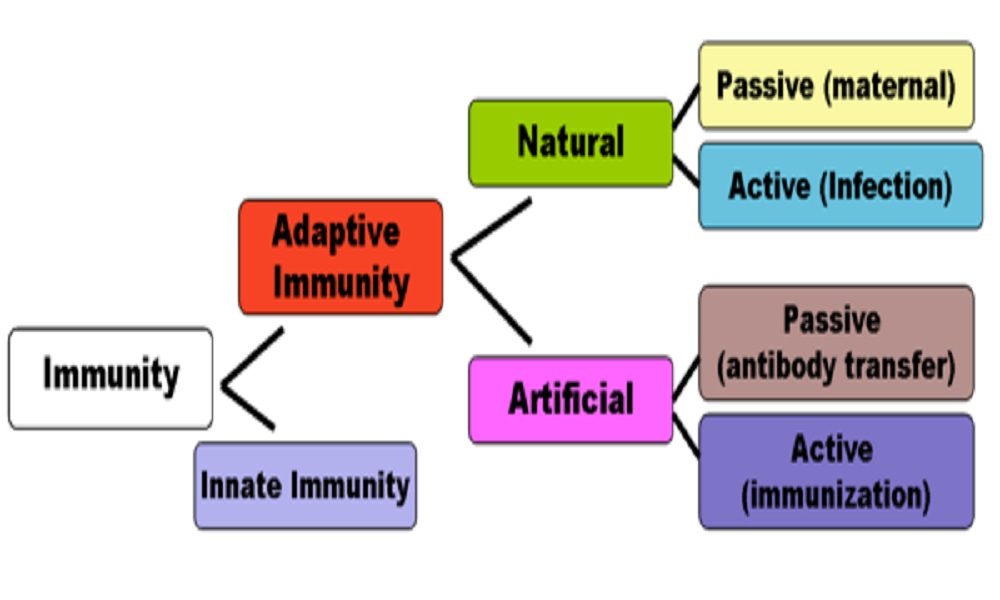
Immunity
Immunity is the ability of an individual host to resists development of disease and allergy even after having received an infective dose of the pathogen with complete virulence and the various allergens.Immune system is the system of animal body which protects it from various pathogens / infectious agents/allergens and cancerImmunology is the science of development…

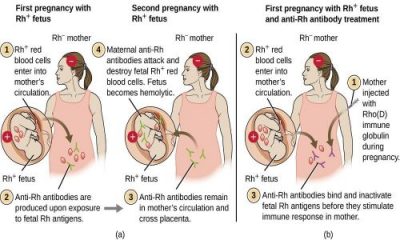
Rh Factor and How it Works
We know that people have different blood types. What this means is some people have one “factor” and some don’t. Some have A, and some have B, and some don’t have either. We call them type A, B and O (think of “zero” if it helps). If you needed a blood transfusion you would have…

Biological Classification
Biological Classification: Understanding the Diversity of Life In the vast tapestry of life that envelops our planet, organisms of all shapes, sizes, and functions coexist. From the towering trees of the rainforests to the microscopic bacteria hidden in the soil, every living entity has a place and role in the intricate web of life. This…