Category: Human anatomy

Did You Know? Your Stomach Gets a New Lining Every Few Days!
Did You Know? Your Stomach Gets a New Lining Every Few Days! 🤯 The human body is full of mind-blowing features, and your stomach is no exception! One of the most fascinating facts about the stomach is that it replaces its lining every 3 to 4 days! But why does this happen? And what would…

General Q&A part-6
State two features of the gas exchange surface in humans? The gas exchange surface in humans primarily refers to the respiratory system, where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place. Two essential features of the gas exchange surface in humans are: Large Surface Area: The gas exchange surface in humans, which includes the…

General Q&A part-5
What are the stages involved in PCR, and on what does PCR depend? Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a widely used molecular biology technique for amplifying specific DNA sequences. PCR involves several stages, and it depends on various components and conditions for successful amplification. Here are the main stages of PCR and what PCR depends…

General Biology MCQs
Here are some biology MCQs. 1. Which organelle is responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells? a) Mitochondria b) Nucleus c) Chloroplasts d) Endoplasmic reticulum Answer: c) Chloroplasts Explanation: Chloroplasts are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis, where plants convert sunlight into chemical energy in the form of glucose. 2. Which of the following is NOT a…

General Q&A part-4
What is oncology? Oncology is the branch of medicine that specializes in the study, diagnosis, treatment, and research of cancer. Cancer is a complex group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body. Oncologists are medical professionals who are trained to diagnose and treat various types of cancer,…

Ventricular Septal Defect: Oxygenation Challenge in Infants
A Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) is a congenital heart defect where a hole exists between the right and left ventricles of the heart. This condition presents a significant challenge for infants as it affects the proper oxygenation of their tissues. This explanation will delve into the details of how a VSD leads to an oxygenation…

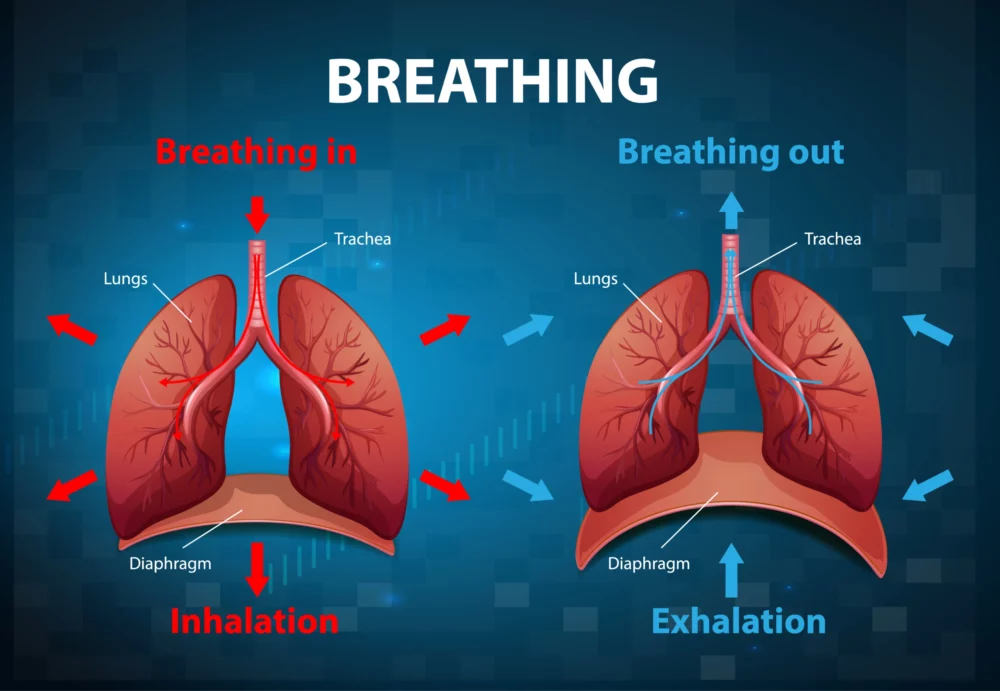
The Respiratory Puzzle: Gaseous Exchange vs. Breathing
Respiration is a fundamental process for all living organisms, ensuring the supply of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide, critical for sustaining life. While “breathing” is a term we commonly associate with the respiratory process, it is essential to recognize that respiration is a multifaceted concept, involving both mechanical actions and intricate physiological processes.…

The Liver’s Role in Regulating Blood Glucose Levels
The liver plays a central and multifaceted role in the regulation of glucose in the human body. Glucose, a simple sugar, serves as the primary source of energy for cells, and maintaining its levels within a narrow range is crucial for overall health. The liver accomplishes this through various mechanisms, which we’ll explore in detail…

General Q&A part-2
This page contains general Q&A questions asked by curious people. What is biochemistry? Biochemistry is a branch of science that combines principles from both biology and chemistry to study the chemical processes and substances that occur within living organisms. It focuses on understanding the molecular mechanisms that underlie various biological functions and processes, including metabolism,…

General Q&A part-1
This page contains general Q&A questions asked by curious people. How many types of Air pollution? Air pollution can be categorized into several types based on the sources of pollutants, the nature of the pollutants, and their effects on the environment and human health. The main types of air pollution include: Particulate Matter (PM): Particulate…

Blood vessels and their functions
Arteries are blood vessels which carry blood away from the heart. They have thick, muscular and elastic walls that can withstand the surge of the high-pressure blood pumped out of the heart.

EXCRETORY SYSTEM IN HUMAN
Except for urinary bladder which is endodermal in origin, the whole excretory system is Except urinary bladder which is endodermal in origin, the whole excretory system is Except mesodermal. In human the kidney is retroperitoneal i.e., the kidney is located outside the coelomic cavity and is covered by peritoneum (coelomic epithelium) from the ventral side…