Category: Biology

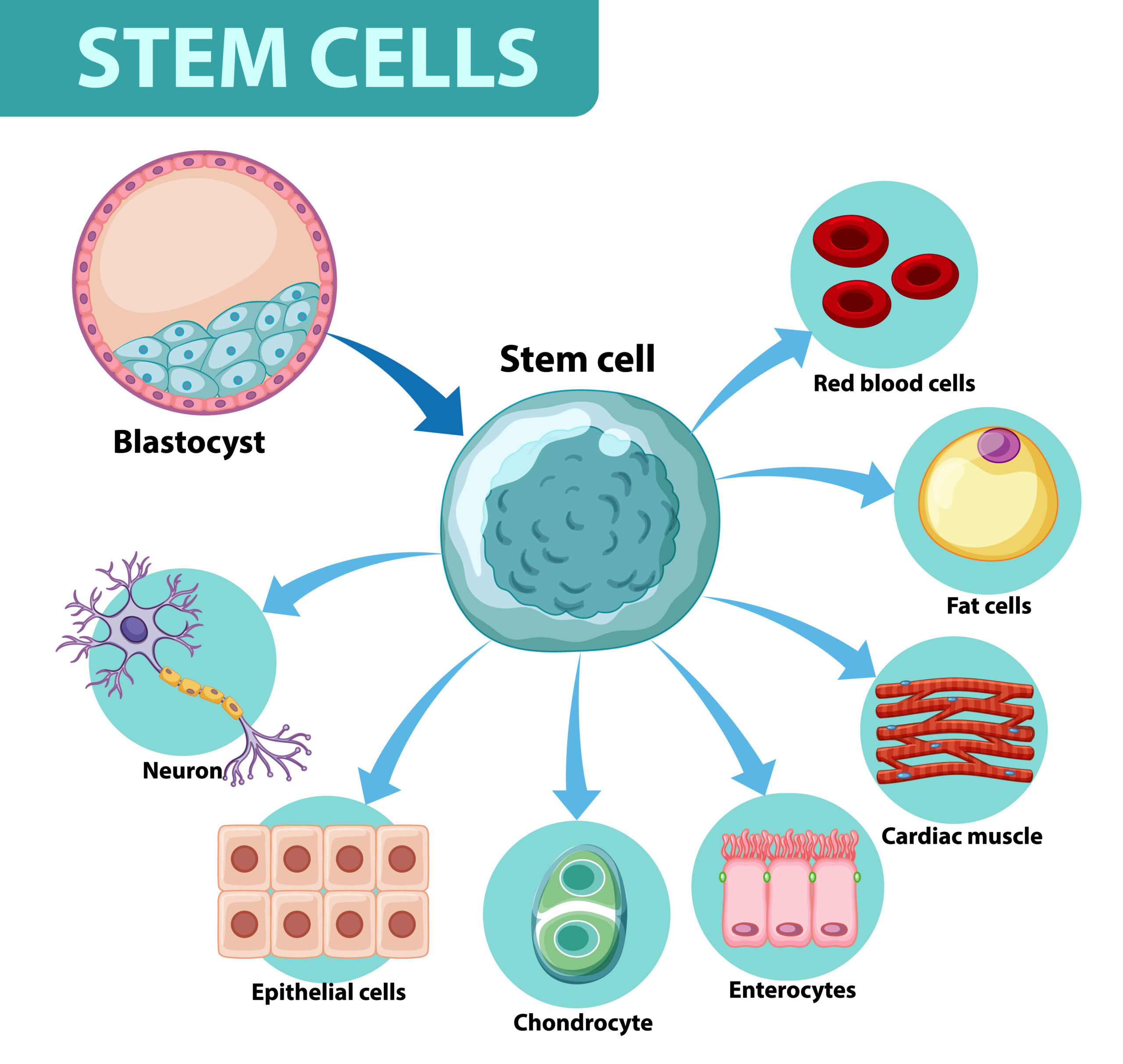
Stem Cells: The Building Blocks of Regeneration
In the intricate tapestry of life, there exists a remarkable group of cells with the potential to reshape our understanding of healing and tissue regeneration. These cells, known as stem cells, have captivated the imagination of scientists and medical researchers for decades due to their unique ability to transform into various cell types and contribute…

Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of the Immune System
1) What is the primary function of the immune system? a) Digestion of food b) Regulation of body temperature c) Protection against infections and diseases d) Production of hormones Answer: c) Protection against infections and diseases Explanation: The immune system’s main role is to defend the body against harmful pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi,…

What is the role of hemoglobin?
The Crucial Role of Hemoglobin in Your Body Hemoglobin is an unsung hero in your body’s complex orchestra of functions. This iron-rich protein plays a central role in sustaining life by carrying oxygen to every cell. Let’s delve into the fascinating functions of hemoglobin and why it’s essential for your well-being. Oxygen Transport – Hemoglobin’s…

What is enzyme and characteristics?
Enzymes are biological catalysts that facilitate chemical reactions in living organisms. They are typically proteins, although some RNA molecules also have catalytic activity. Enzymes are essential for life because they speed up the reactions that are necessary for cells to function properly. Without enzymes, many biochemical reactions in the body would occur too slowly to…

MCQ on Breathing and Exchange of Gases-2
Visiting high mountains may cause altitude sickness in men living in plain areas. Prime cause of this is (a) excess of CO2 in blood (b) decreased efficiency of haemoglobin (c) decreased partial pressure of oxygen (d) decreased proportion of oxygen in air. Increase in body temperature makes oxygen haemoglobin dissociation curve (a) shift to left…

Why Earthworms Are a Gardener’s Best Friend
Earthworms are considered a gardener’s best friend for several reasons: Soil aeration: Earthworms burrow through the soil, creating tunnels and air pockets that allow air, water, and nutrients to penetrate the soil more easily. This improves soil aeration, which is important for plant root health. Soil structure: Earthworms also help to improve soil structure by…

Koala Has Human Like Fingerprints!
The discovery that koalas have human-like fingerprints was a surprising revelation that has captured the attention of the scientific community and the general public alike. In this essay, I will explain this discovery in detail, including the methods used by researchers to uncover this fact and the potential implications of this discovery for the field…

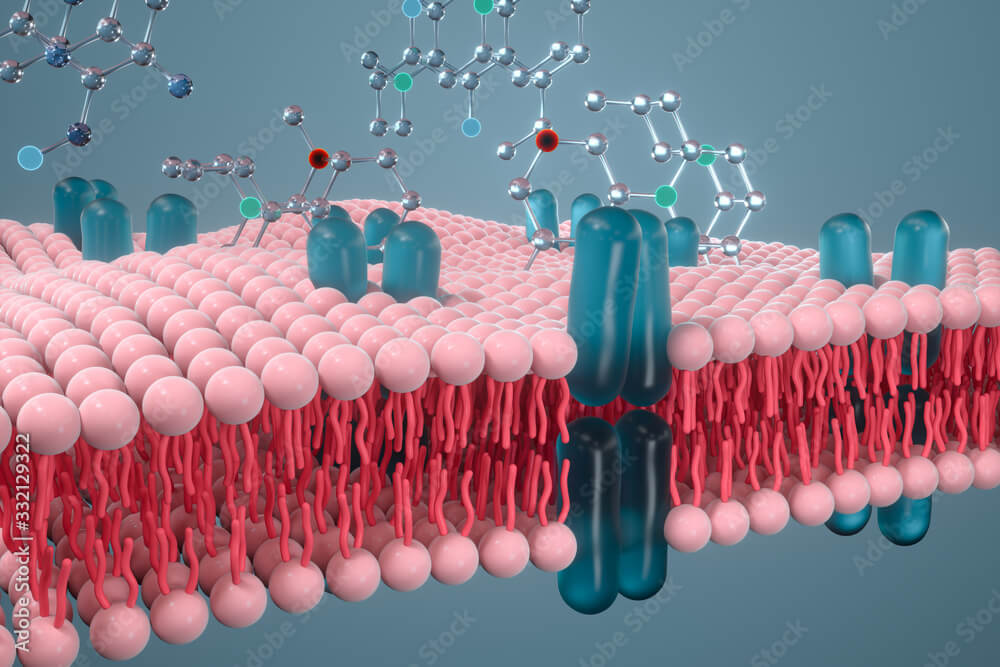
Plasma membrane
Delimiting membrane or boundary of all cells providing the characteristic shape to the cell. Structure ● Composed of approx. 7 nm thick phospholipid bilayer with hydrophilic heads facing outward from both sides into aqueous environment and hydrophobic tails facing inside the bilayer. ● A symmetrical the presence of proteins, floating in the bilayer imparts a…

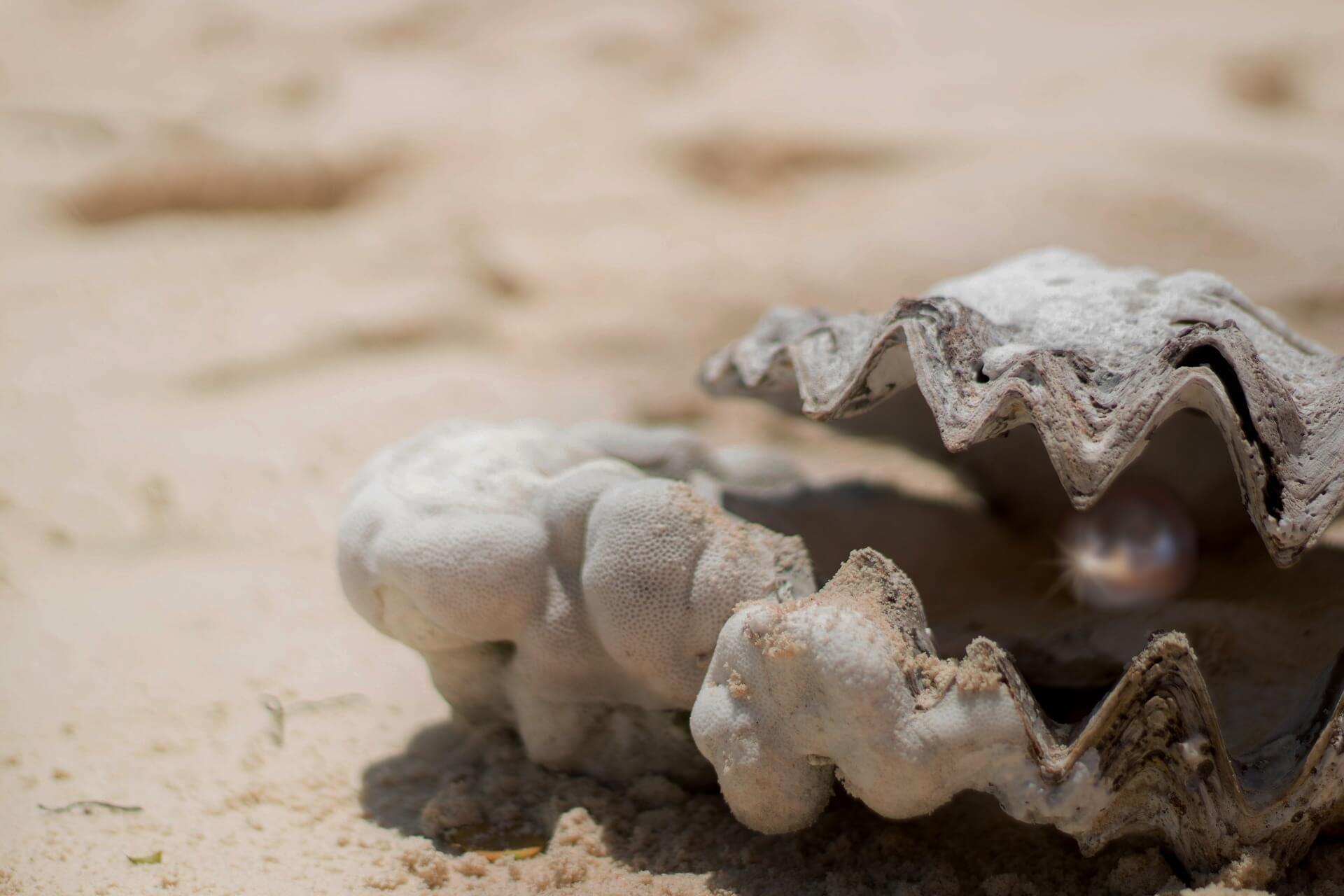
How do oysters make pearls?
Pearls are formed in the body of a sea oyster as a response to an irritant that enters its shell. The irritant can be a foreign object such as a grain of sand or a parasite that makes its way into the oyster’s shell. In response to the irritant, the oyster secretes a substance called…

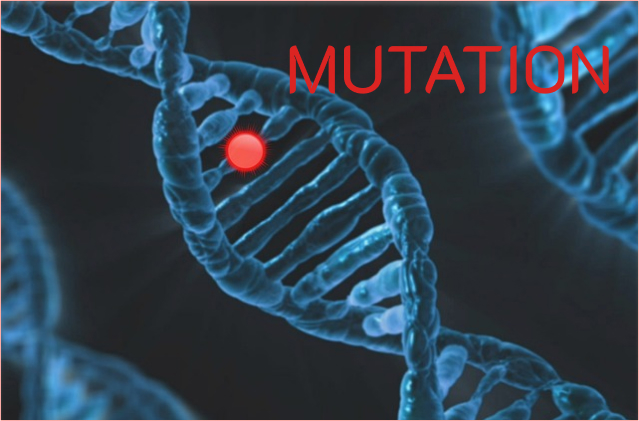
Mutation
Mutation is a change in the DNA sequence of an organism’s genetic material. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the molecule that carries the genetic instructions for the development and function of all living things. DNA is made up of four chemical bases, adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T), which are arranged in…

Chromosome
A chromosome is a structure found in cells that is made up of a long strand of DNA, which is the genetic material that contains the instructions for the development and function of all living organisms. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and play a crucial role in the cell cycle, replication,…

Defences Against Diseases
The body has three main lines of defence against disease. These involve mechanical barriers, chemical barriers and cells. Mechanical barriers Although many bacteria live on the surface of the skin, the outer layer of the epidermis seems to act as a barrier that stops them getting into the body. But if the skin is cut…