Category: Biology

Ventricular Septal Defect: Oxygenation Challenge in Infants
A Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) is a congenital heart defect where a hole exists between the right and left ventricles of the heart. This condition presents a significant challenge for infants as it affects the proper oxygenation of their tissues. This explanation will delve into the details of how a VSD leads to an oxygenation…

General Q&A part-3
Why a camel have long loop of Henle? Camels have evolved to survive in harsh desert environments, where water is often scarce and temperatures can be extremely high. One of the adaptations that helps camels conserve water is their long loop of Henle in their kidneys. The loop of Henle is a part of the…

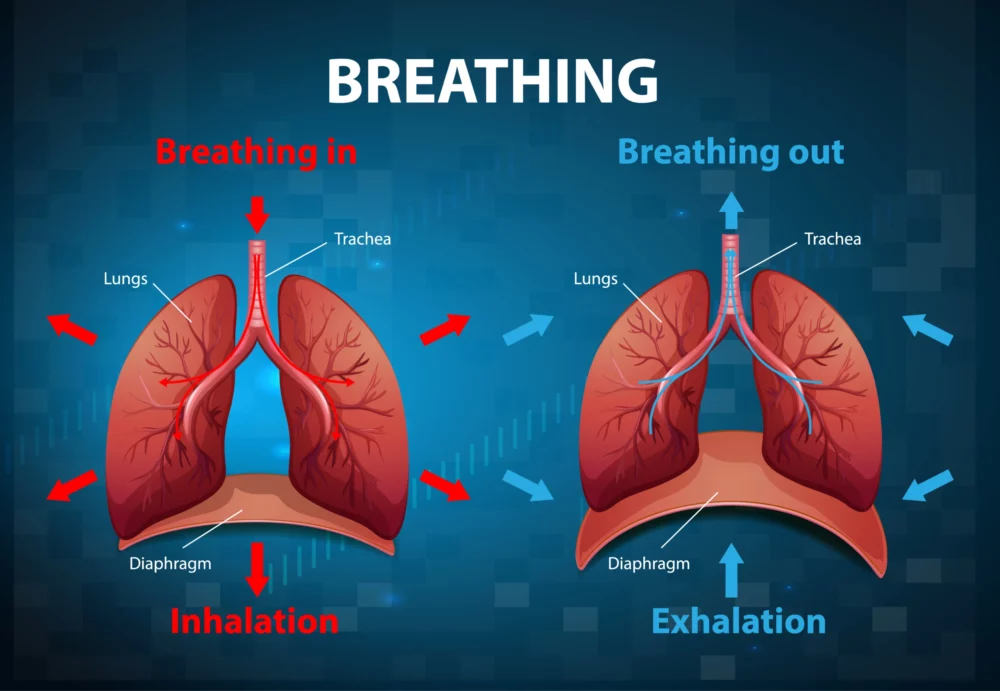
The Respiratory Puzzle: Gaseous Exchange vs. Breathing
Respiration is a fundamental process for all living organisms, ensuring the supply of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide, critical for sustaining life. While “breathing” is a term we commonly associate with the respiratory process, it is essential to recognize that respiration is a multifaceted concept, involving both mechanical actions and intricate physiological processes.…

The Liver’s Role in Regulating Blood Glucose Levels
The liver plays a central and multifaceted role in the regulation of glucose in the human body. Glucose, a simple sugar, serves as the primary source of energy for cells, and maintaining its levels within a narrow range is crucial for overall health. The liver accomplishes this through various mechanisms, which we’ll explore in detail…

Exploring the Role of Potted Plants in Scientific Research
Plants have always held a central place in scientific research due to their essential role in the natural world. However, when it comes to studying plant biology, ecology, environmental science, and even aspects of human health, one tool frequently makes an appearance—the potted plant. These humble containers of soil and greenery serve as valuable assets…

Why Humans Can’t Grow Horns?
The claim that human beings are capable of growing horns, particularly during young ages, is a widely circulated but inaccurate belief. This misconception likely stems from a misunderstanding of human biology and the regenerative capabilities of stem cells, as well as a lack of awareness about the specific genetic, developmental, and physiological factors that determine…

General Q&A part-2
This page contains general Q&A questions asked by curious people. What is biochemistry? Biochemistry is a branch of science that combines principles from both biology and chemistry to study the chemical processes and substances that occur within living organisms. It focuses on understanding the molecular mechanisms that underlie various biological functions and processes, including metabolism,…

General Q&A part-1
This page contains general Q&A questions asked by curious people. How many types of Air pollution? Air pollution can be categorized into several types based on the sources of pollutants, the nature of the pollutants, and their effects on the environment and human health. The main types of air pollution include: Particulate Matter (PM): Particulate…

What is a photochemical smog?
Photochemical smog forms when certain pollutants in the atmosphere react with sunlight. It mainly consists of ground-level ozone (O3), mixed with other toxic gases and particulate matter. This type of air pollution typically plagues urban areas, especially in cities with high levels of vehicle and industrial emissions. Here’s how photochemical smog forms: Emissions: It all…

Q&A on plant structure and function
Q: What is the primary function of plant leaves? A: The primary function of plant leaves is to perform photosynthesis, where they convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen. Additionally, leaves also facilitate gas exchange and transpiration. Q: How do plant roots contribute to the overall health of a plant? A: Plant…

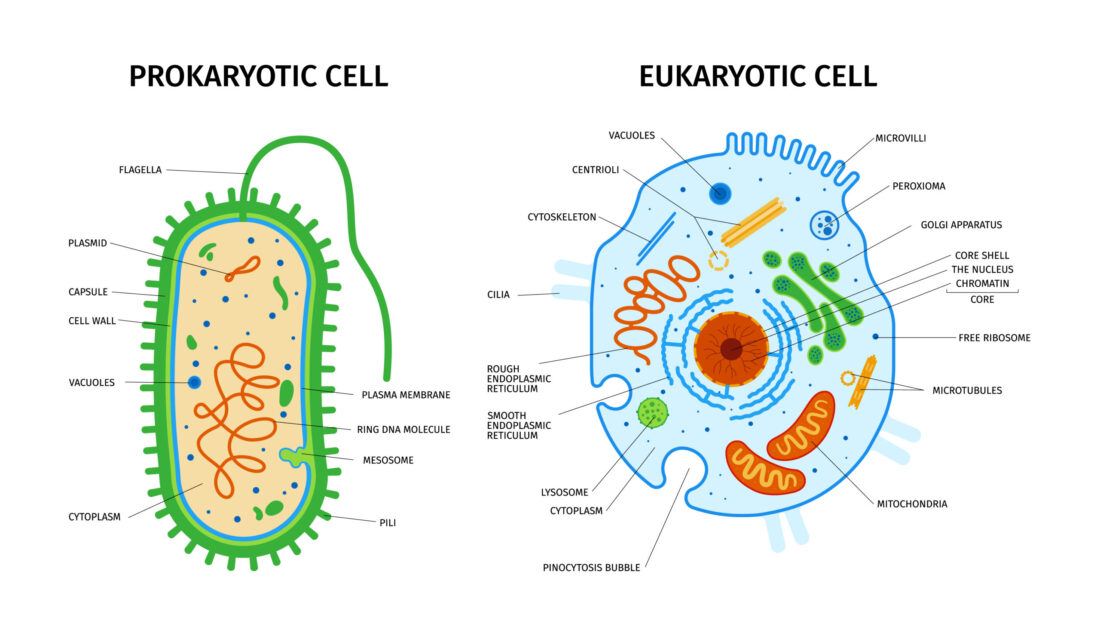
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
In the intricate world of biology, cells come in two major types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. These cells serve as the building blocks of life, but they differ significantly in structure and how they function. Understanding the contrasts between these cell types not only sheds light on the diversity of life but also reveals the fascinating…

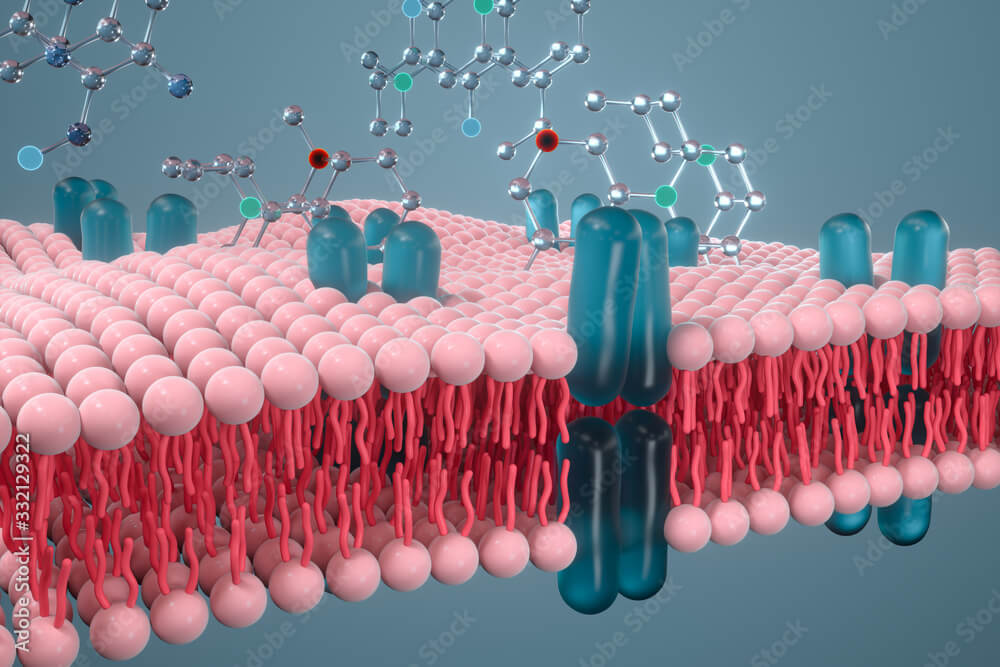
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function: Key Role in Cell Homeostasis
The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, is a crucial structure that surrounds all living cells. It separates the internal environment of the cell from the extracellular environment, regulating the flow of substances in and out of the cell. The plasma membrane plays a central role in maintaining cell homeostasis, which is the…