Category: A level biology

Ventricular Septal Defect: Oxygenation Challenge in Infants
A Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) is a congenital heart defect where a hole exists between the right and left ventricles of the heart. This condition presents a significant challenge for infants as it affects the proper oxygenation of their tissues. This explanation will delve into the details of how a VSD leads to an oxygenation…

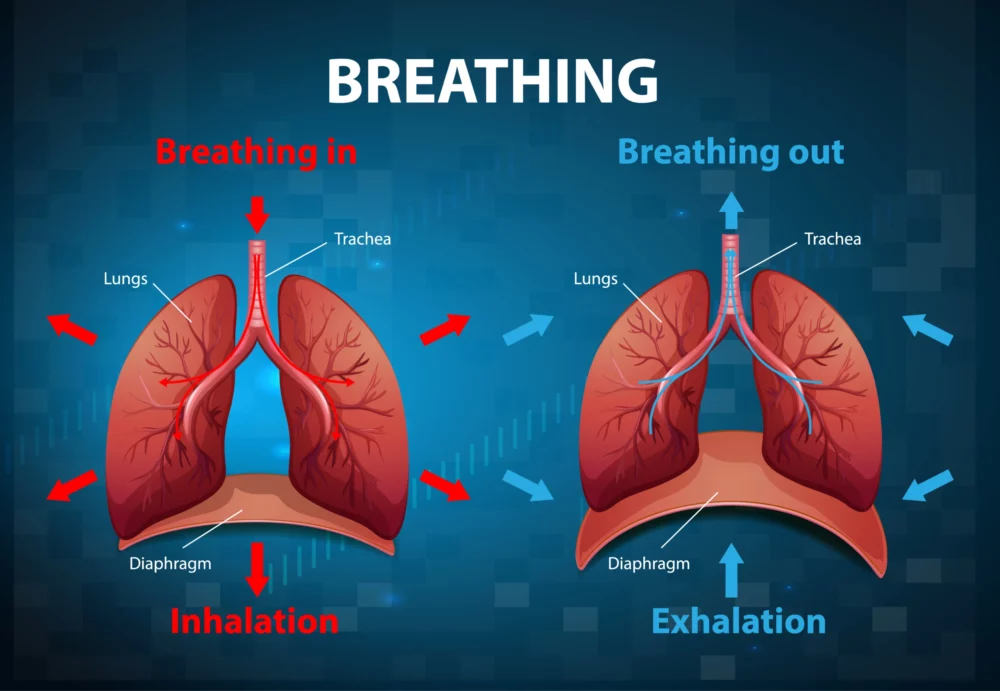
The Respiratory Puzzle: Gaseous Exchange vs. Breathing
Respiration is a fundamental process for all living organisms, ensuring the supply of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide, critical for sustaining life. While “breathing” is a term we commonly associate with the respiratory process, it is essential to recognize that respiration is a multifaceted concept, involving both mechanical actions and intricate physiological processes.…

General Q&A part-2
This page contains general Q&A questions asked by curious people. What is biochemistry? Biochemistry is a branch of science that combines principles from both biology and chemistry to study the chemical processes and substances that occur within living organisms. It focuses on understanding the molecular mechanisms that underlie various biological functions and processes, including metabolism,…

Q&A on plant structure and function
Q: What is the primary function of plant leaves? A: The primary function of plant leaves is to perform photosynthesis, where they convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen. Additionally, leaves also facilitate gas exchange and transpiration. Q: How do plant roots contribute to the overall health of a plant? A: Plant…

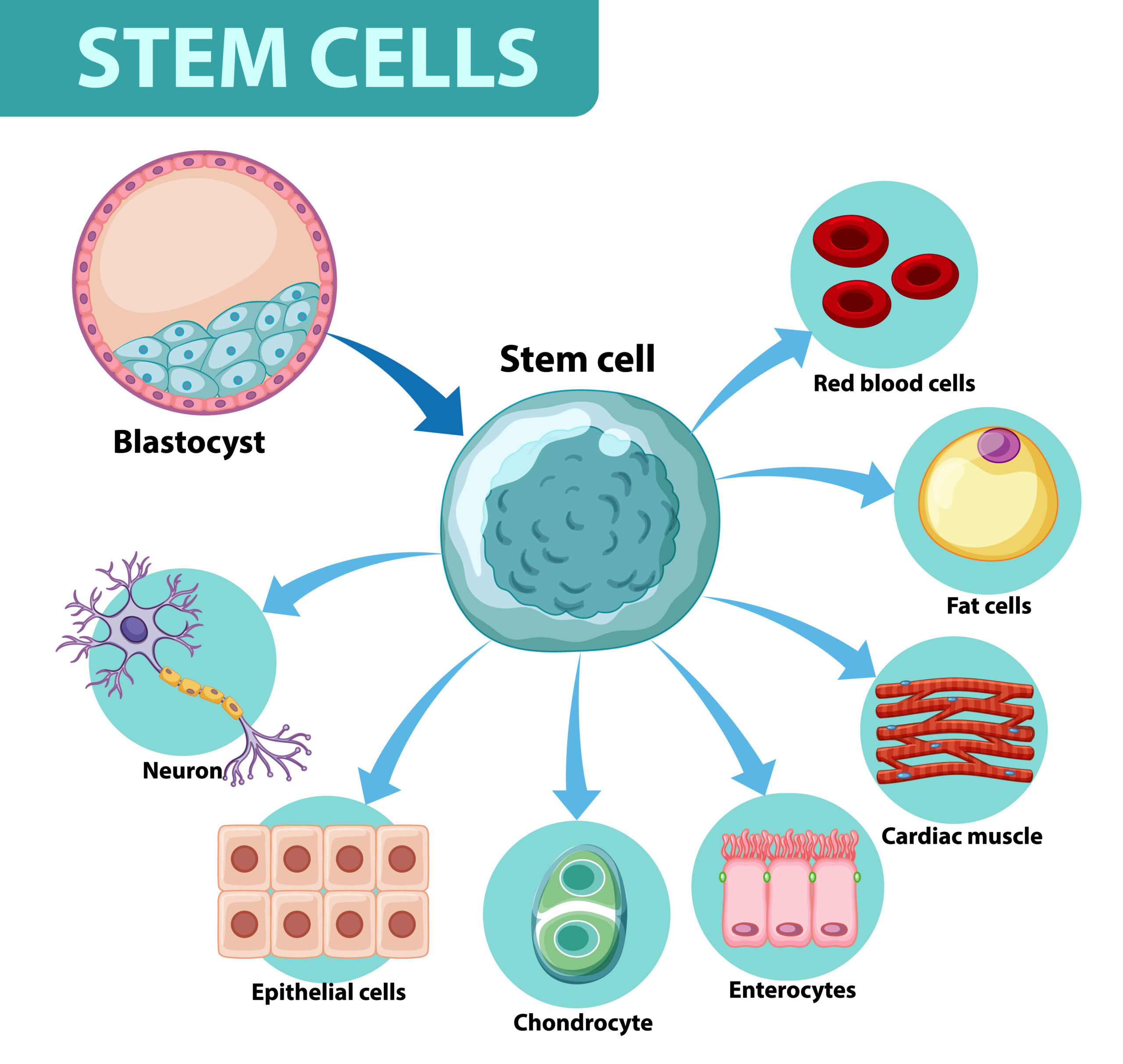
Stem Cells: The Building Blocks of Regeneration
In the intricate tapestry of life, there exists a remarkable group of cells with the potential to reshape our understanding of healing and tissue regeneration. These cells, known as stem cells, have captivated the imagination of scientists and medical researchers for decades due to their unique ability to transform into various cell types and contribute…

Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of the Immune System
1) What is the primary function of the immune system? a) Digestion of food b) Regulation of body temperature c) Protection against infections and diseases d) Production of hormones Answer: c) Protection against infections and diseases Explanation: The immune system’s main role is to defend the body against harmful pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi,…

What is enzyme and characteristics?
Enzymes are biological catalysts that facilitate chemical reactions in living organisms. They are typically proteins, although some RNA molecules also have catalytic activity. Enzymes are essential for life because they speed up the reactions that are necessary for cells to function properly. Without enzymes, many biochemical reactions in the body would occur too slowly to…

MCQ on Breathing and Exchange of Gases-2
Visiting high mountains may cause altitude sickness in men living in plain areas. Prime cause of this is (a) excess of CO2 in blood (b) decreased efficiency of haemoglobin (c) decreased partial pressure of oxygen (d) decreased proportion of oxygen in air. Increase in body temperature makes oxygen haemoglobin dissociation curve (a) shift to left…

Why Earthworms Are a Gardener’s Best Friend
Earthworms are considered a gardener’s best friend for several reasons: Soil aeration: Earthworms burrow through the soil, creating tunnels and air pockets that allow air, water, and nutrients to penetrate the soil more easily. This improves soil aeration, which is important for plant root health. Soil structure: Earthworms also help to improve soil structure by…

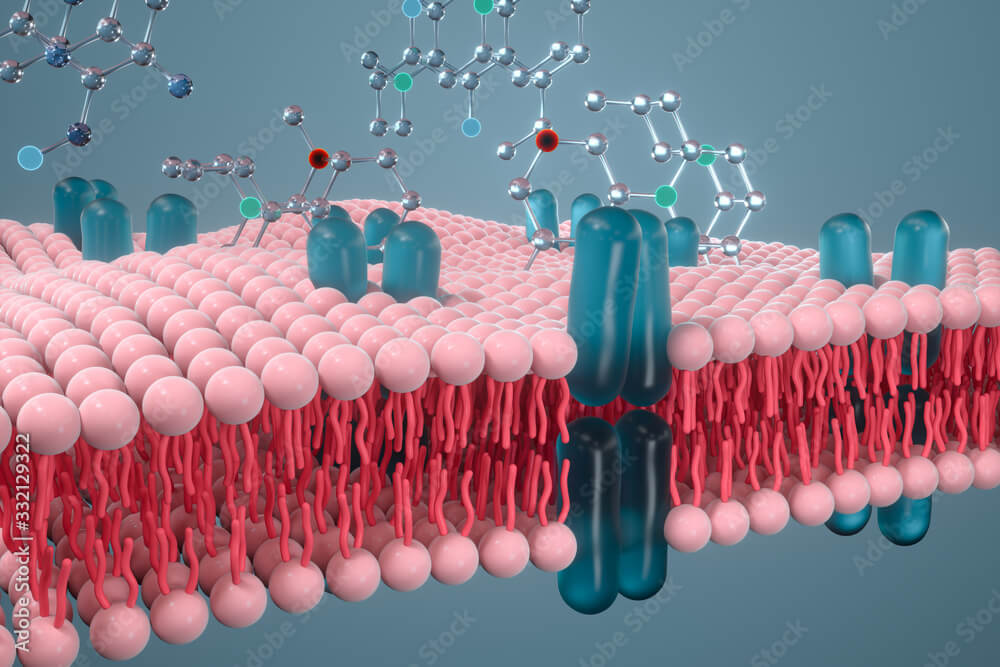
Plasma membrane
Delimiting membrane or boundary of all cells providing the characteristic shape to the cell. Structure ● Composed of approx. 7 nm thick phospholipid bilayer with hydrophilic heads facing outward from both sides into aqueous environment and hydrophobic tails facing inside the bilayer. ● A symmetrical the presence of proteins, floating in the bilayer imparts a…

Mutation
Mutation is a change in the DNA sequence of an organism’s genetic material. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the molecule that carries the genetic instructions for the development and function of all living things. DNA is made up of four chemical bases, adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T), which are arranged in…

Chromosome
A chromosome is a structure found in cells that is made up of a long strand of DNA, which is the genetic material that contains the instructions for the development and function of all living organisms. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and play a crucial role in the cell cycle, replication,…